Ahead of today’s much-anticipated quarterly refunding announcement by the US Treasury, some were hopeful that Bessent could pull an anti-Yellen and forecast a gradual decline in long-term issuance in coming quarters, sending yields lower. None of the happened, however, and instead the Treasury did not surprise markets, announcing that this quarter’s refunding total would come in line with estimates, at $125BN (to refund $90.2BN in securities). And while the Treasury said that auction sizes would be unchanged for “next several quarters” as expected, the department said it would continue to rely on bills to fund the increasing amount of federal spending. That said, by late March, the Treasury anticipates incrementally reducing short-dated bill auction sizes in light of the April 15 tax date. These reductions will lead – the Treasury believes – to a cumulative $250-300 billion net decline in total bill supply by early May.
Here is a summary of what the Treasury announced:
No surprises in today’s Refunding statement
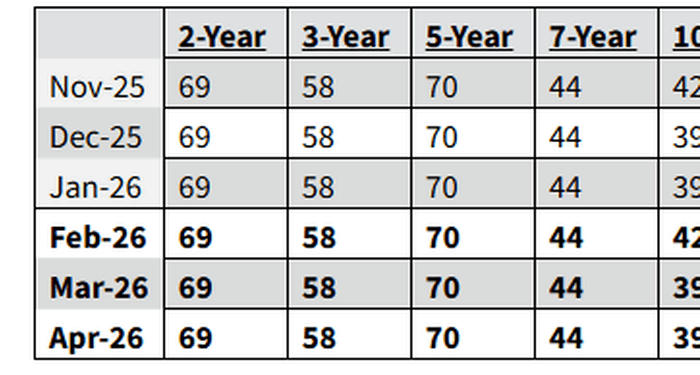
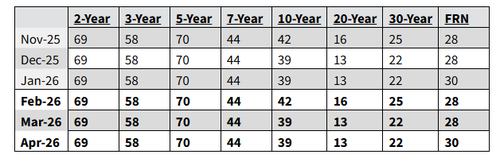
- No change in net issuance: Treasury says will keep coupon, floating rate note auction sizes unchanged for “next several quarters” as expected. No ramp in issuance yet.
- Refunding size: Treasury offering $125BN in quarterly refunding, as expected. Will sell $58BN in 3Y, $42BN in 10Y and $25BN in 30Y, and will keep auctions sizes unchanged through May.
- Bills: Despite QE Lite, the Treasury expects to “maintain the offering sizes of benchmark bills at current levels into mid-March” By late March, Treasury anticipates incrementally reducing short-dated bill auction sizes in light of the April 15 tax date. These reductions will lead to a cumulative $250-300 billion net decline in total bill supply by early May
- Cash: Treasury assumes an $850BN cash balance at the end of March. However, based on current projections for the upcoming refunding quarter, Treasury estimates that the size of the Treasury General Account (TGA) could peak around $1,025 BN by late April.
- Buybacks: Treasury expects to purchase up to $38BN in off-the-run securities across buckets for “liquidity support” and up to $75 billion in the 1-month to 2-year bucket for cash management purposes in the coming quarter.
Taking a closer look at the Treasury’s quarterly refunding statement published at 8:30am Wednesday, the department said it anticipated keeping auction sizes unchanged for nominal notes, bonds and floating-rate notes, “for at least the next several quarters”, a paraphrase of the same forward guidance that debt managers have used for two years now.
As for next week’s refunding auctions, they will total $125 billion, as expected, and will be made up of:
- $58 billion of 3-year notes on Feb. 10
- $42 billion of 10-year notes on Feb. 11
- $25 billion of 30-year bonds on Feb. 12
The refunding will raise new cash of approximately $34.8BN, net of the $90.2BN in maturing securities.
The Treasury also said it’s “monitoring” the Federal Reserve’s expanded purchases of bills, which mature in a year or less. The central bank in December stunned markets (if not ZH readers, who knew about the move well ahead of time), when it said it would buy $40 billion a month of Bills until April, in an effort to ensure ample reserves in the banking system. And the department is keeping an eye on “growing demand for Treasury bills from the private sector.”
As a result, based on current fiscal forecasts, Treasury expects to maintain the offering sizes of benchmark bills at or near current levels into mid-March. By late March, Treasury anticipates incrementally reducing short-dated bill auction sizes in light of the April 15 tax date. These reductions will likely lead to a cumulative $250-300 billion net decline in total bill supply by early May. The Treasury “will continue to evaluate near-term borrowing needs and assess additional adjustments to bill auction sizes as appropriate.”
The department has for several quarter relied on T-Bills to fund the steadily increasing amount of federal spending. Amid that focus, some market participants ahead of Wednesday’s release reported speculation of aggressive moves to outright reduce bond issuance to help pull down yields that serve as a benchmark for mortgages and other loans. That did not happen.
Separately, the Treasury also “continues to evaluate potential future increases to nominal coupon and FRN auction sizes, with a focus on trends in structural demand and potential costs and risks of various issuance profiles,” the department said. FRNs refer to floating rate notes.
“While the administration’s focus on affordability measures has brought back questions about potential efforts to lower borrowing costs via more active adjustments to the issuance mix, we do not expect Treasury to do so at this point,” Goldman Sachs strategists William Marshall and Bill Zu wrote ahead of Wednesday’s release. Goldman’s take reflected the views of many dealers. Any move to cut sales of bonds, or 10-year notes, would have run against the department’s long-standing pledge to be “regular and predictable” in its debt management. Bessent himself invoked that language in a speech in November.
“The statement itself was very much steady-as-she-goes, with the Treasury reiterating the view that nominal coupon and FRN auction sizes will hold ‘for at least the next several quarters,’” said John Canavan, lead analyst at Oxford Economics.
Meantime, the Fed’s purchases reduce “the risk of Treasury oversupplying” the market with more bills than investors are prepared to handle, Morgan Stanley strategists led by Martin Tobias wrote in their refunding preview. Beyond April, the Fed’s plans are unclear, however — all the more so given Kevin Warsh’s nomination to become the next chair in May. Warsh has in the past advocated shrinking the Fed’s securities portfolio.
Two more things to note:
While the Treasury assumes an $850 billion cash balance at the end of March, based on current projections for the upcoming refunding quarter, the Treasury now estimates that the size of the Treasury General Account (TGA) could peak around $1,025 billion (plus or minus $50 billion) by late April, before declining rapidly in May after tax day (this estimate reflects significant uncertainty regarding the size of April tax receipts, as well as macroeconomic factors and the path of fiscal and monetary policy).
Additionally, as part of its quarterly Treasury buyback schedule release, the Treasury said it anticipates that, over the course of the upcoming quarter, it will purchase up to $38 billion in off-the-run securities across buckets for liquidity support and up to $75 billion in the 1-month to 2-year bucket for cash management purposes.
Loading recommendations…